The Human Eye Cannot Perceive Objects Less Than
A normal eye cannot see clearly the objects that are placed closer than 25cm because the power of accommodation of the eye is 25cm which is exhausted. I dont blame them however.
The Human Eye Can See Infrared Light Plus 5 Other Things You Had No Idea Eyes Can Do Insight Eye Specialists Utah Lasik And Cataract Doctors
25cm distance for normal eye.

. The human eye cannot see clearly at a distance which is less than a 25 cm b 25 cm c 15 cm d 15 cm. When the maximum accommodation of the eye is reached the ciliary muscles of the eye lens cannot become thicker. Blurred vision A condition often caused by myopia hyperopia astigmatism.
A Identify the defect of vision. Microscope that shines light through a specimen and has two lenses to magnify an image. I blame the dictionary.
That means the spectacle lens must produce an image 300 cm from the eye for an object very far away. A person cannot see the objects distinctly when placed at a distance less than 50 cm. An image 300 cm from the eye will be 285 cm to the left of the spectacle lens see Figure 2.
E The two stars will look like a single point of light. Whoever asked this question completely misunderstands colors and in fact the entire visual process. Hence we cannot clearly see an object kept at a distance less than 25 cm from the eye.
Remember a converging lens is required to correct far sightedness. Q2 CBSE 2011. Determine the focal length of contact lenses that will enable this person to read a magazine at a distance of 25 cm.
01 mm in diameter. A far sighted person person cannot see clearly objects that are closer to the eye than 73 cm. A person cannot see clearly objects more than 700 cm away.
Relative clarity The monocular cue that states that distant objects are less clear than nearby objects are. Without clear depth cues from both eyes the brain cannot produce a clear three-dimensional image with depth or stereopsis. This is due to.
One to receive light from each of the points and. He is suffering from. Human Eye and Colourful World.
A You will not be able to see these two stars at all. For a young adult with normal vision the near point is about 25 cm. Since the eyes point in different directions the brain cannot form a three-dimensional picture of the object.
The minimum distance at which objects can be seen most distinctly without strain is called the least distance of distinct vision. Make a diagram to show how hypermetropia is corrected. B The two stars will appear to be touching looking rather like a small dumbbell.
Answer 1 of 8. Find the nature the focal length and the power of the correcting lens. When an object kept at a distance less than 25 cm then it will look blur because focal length of eyes will not decrease more than 25 cm.
The human eye cannot perceive objects objects less than. The image distance is negative because it. Red has the lowest energy and violet the highest.
The minimum distance of an object from a normal eye for which the eye lens can decrease its focal length to the least possible value is 25 cm. To perceive two separate points at least three photoreceptors arranged in a row are required. Beyond red and violet are many other kinds of light our human eyes cant see much like there are sounds our ears cant hear.
What power of lens should be prescribed if the glass is to be worn 100 cm in front of the eye. C You will see two distinct stars. As a result the curvature of the eye lens does not occur beyond a certain limit and the image is not formed exactly on the retina so the object becomes blur and hazy when it is held closer to the eye.
The human eye cannot perceive objects less than ----- in size. C Calculate the power and nature of the lens he should be using to see clearly the object placed at a distance of 25 cm from his eyes. This question is so so wrong on so many levels I really dont even know where to start.
Therefore we must get d i 285 cm when d o. The human eye can focus objects at different distances by adjusting the focal length of the eye lens. B Give two reasons for this defect.
Which objective lens provides the least total magnification. A man is unable to see objects distinctly at a distance less than 1 metre. D You will see only the larger of the two stars not the smaller one.
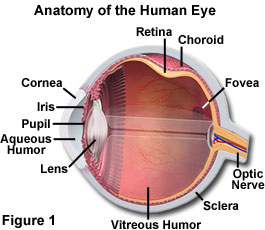
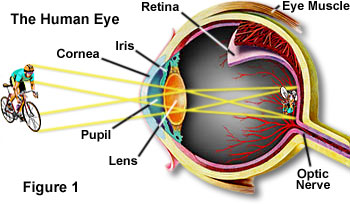
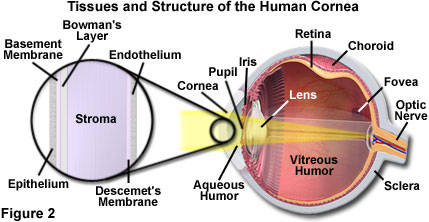
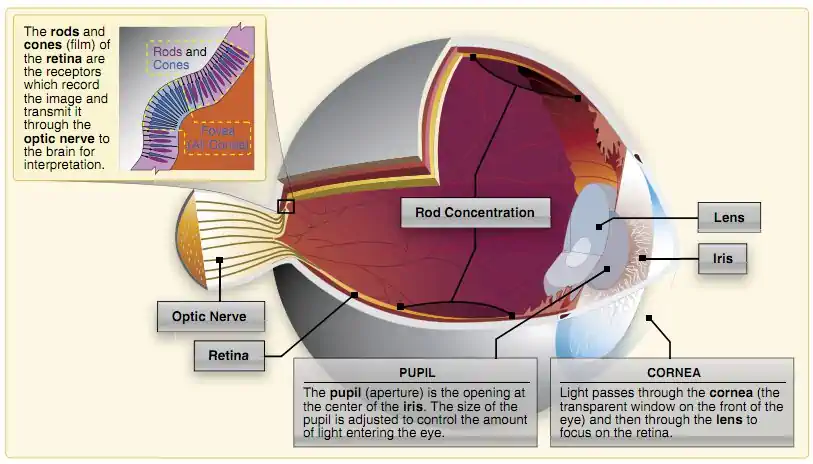
Structure of the Eye. The near point of a. The angular resolution of the human eye typically ranges between 40 arcseconds and 1 arcminute.
A normal eye cannot see an object when placed closer than 25 cm because the ciliary muscles after a certain limit ie upto 25 cmcannot perform contraction or relaxation. You want this nearsighted person to be able to see very distant objects clearly. What are the two lenses of the compound light microscope called.
That is the focal length of the lens is positive. The objective lenses of the compound light microscope are attached to the. On one end of the electromagnetic spectrum are radio waves which have wavelengths billions of times longer than those of visible light.
Also called overlap it refers to the cue for depth perception when one object A covers or overlaps another object B and we see object A as being in front. Asked Jan 21 2018 in Physics by Kundan kumar 512k points A person cannot see objects beyond 80 cm from his eye while a person with normal eyesight can see object easily placed upto 160 cm from the eye. It is also called the near point of the eye.
Molecular Expressions Microscopy Primer Physics Of Light And Color Human Vision And Color Perception
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/13619648/VXC_Samsung_Article2_LeadIllo_12.11.18.jpg)
How The Human Eye Processes Pixels The Verge
Molecular Expressions Science Optics And You Light And Color Human Vision And Color

Human Vision And Why The Colour Green Is So Important
Molecular Expressions Microscopy Primer Physics Of Light And Color Human Vision And Color Perception

Can The Human Eye See 8k And Do We Really Need 8k Tv Paul Maguire

What S Inside The Human Eye Plano Tx Impact Eyecare

All The Colors We Cannot See Tetrachromacy In Humans By Carl Jennings The Startup Medium
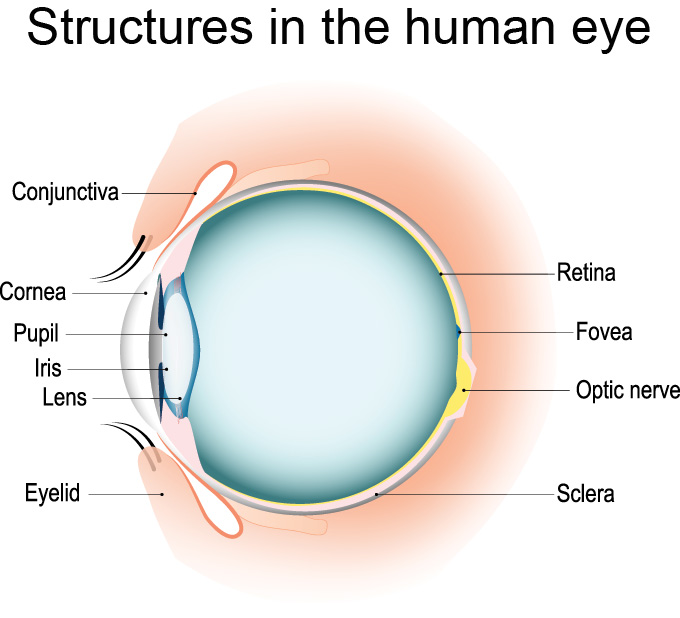
Explainer How Our Eyes Make Sense Of Light Science News For Students
![]()
The Camera Versus The Human Eye Petapixel
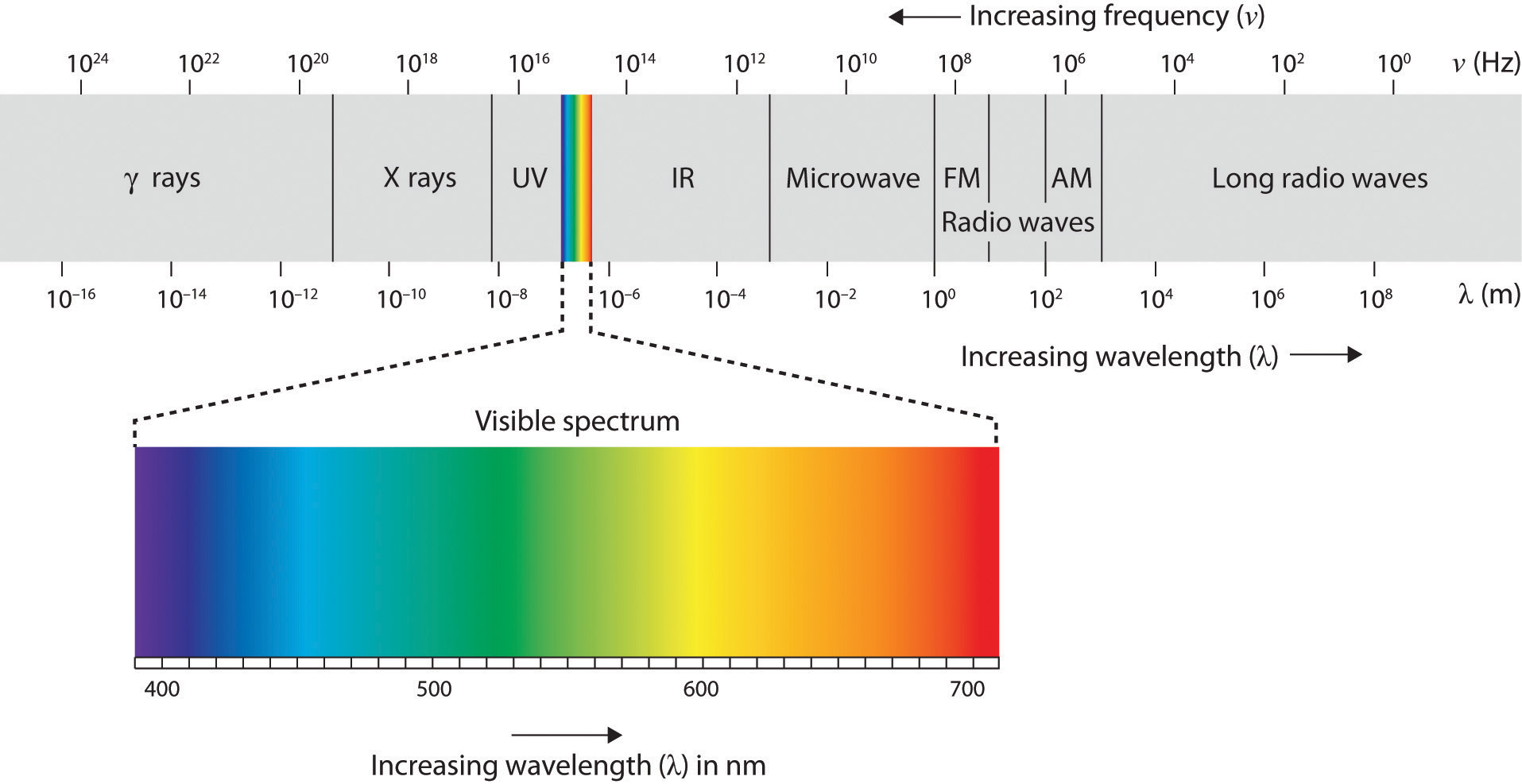
4 2 Seeing Introduction To Psychology

How The Human Eye Works Live Science
5 2 Seeing Introduction To Psychology 1st Canadian Edition

Explainer How Our Eyes Make Sense Of Light Science News For Students

The Human Eye Boundless Physics

How The Human Eye Differentiate Between Distant Objects Britannica
Comments
Post a Comment